Overview of the Gateway® Cloning
Gateway® technology is an in vitro cloning strategy that is based on the recombination of specific recombination sites, namely attP in phage and attB in E. coli. Through a two-step process, any gene or DNA fragment can easily be cloned in a directional and reversible manner into an entry vector before transferring into a destination vector for expression. The following describes the molecular events involved in Gateway cloning:
Step1: Cloning the gene of interest into an entry vector
The first step involves generating a gene or DNA fragment with flanking attB1 and attB2 recombination sites. This can be achieved through PCR, restriction enzyme digestion, a cDNA library or a synthetic DNA fragment like GenParts™ DNA Fragments. Similarly, corresponding attP1 and attP2 recombination sites need to be generated in the recipient vector, called pDonor. After mixing the fragment and vector with the BP Clonase enzyme mix, the enzyme catalyzes the site-specific recombination to generate an entry vector containing the insert flanked by attL1 and attL2 sites (Fig. 1). This vector can now be used to transfer the gene of interest into any Gateway destination vector for expression.
https://blog.addgene.org/plasmids-101-gateway-cloning
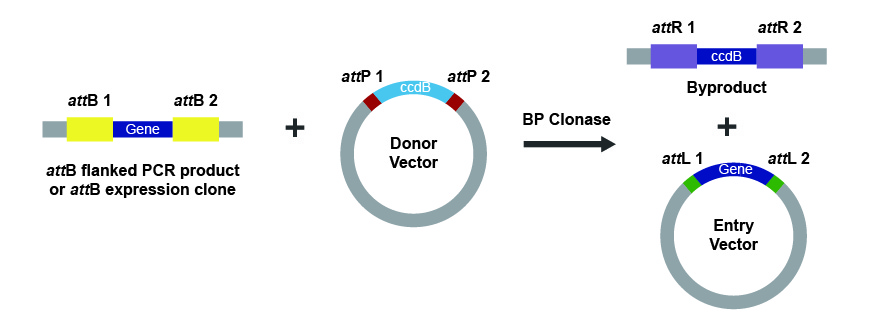
Figure 1. The BP Clonase reaction as the first step in Gateway cloning.
Step2: Subcloning the gene of interest into a destination vector
In this step, the entry vector is mixed with the LR Clonase enzyme mix and a destination vector containing attR1 and attR2 recombination sites. The result of the enzymatic activity is a vector containing the gene of interest flanked by its original attB1 and attB2 and ready for transformation and expression in any desired host organism.
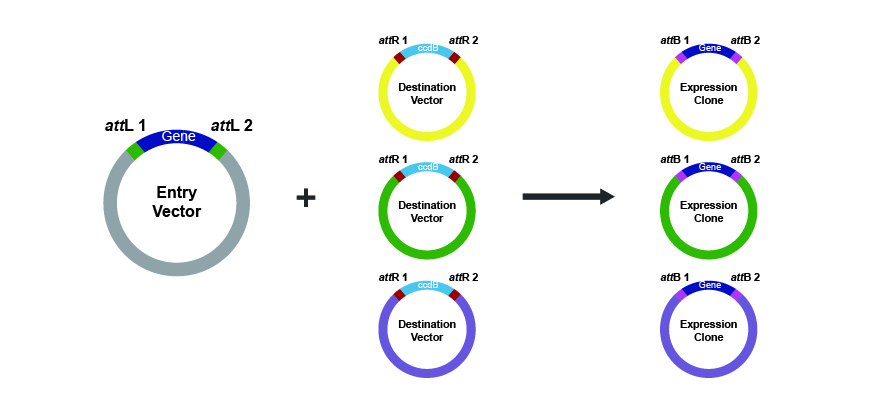
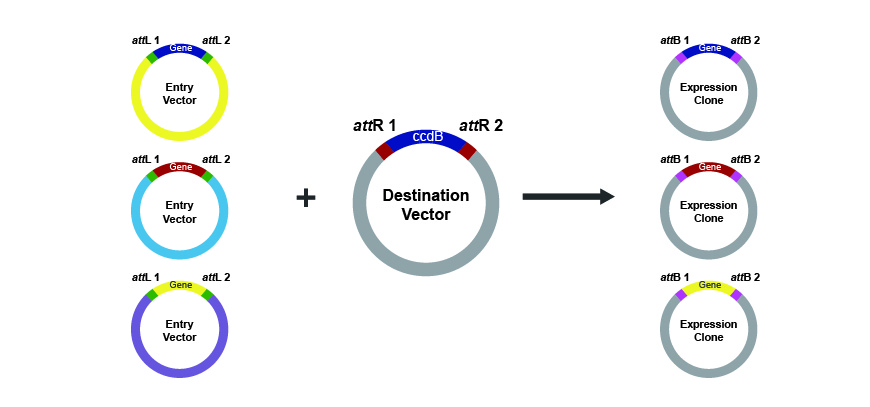
Figure w. The LR Clonase reaction as the second step in Gateway cloning.
In this system, presence of an antibiotic resistant marker in the entry and destination vectors along with the toxic ccdB gene in the destination vector allows for efficient screening of positive clones.
Applications and Advantages of Gateway® Cloning
This cloning strategy can be used in any downstream application that requires the transfer of one gene or DNA fragment into different types of plasmids for bacterial, mammalian or insect expression, or thousands of genes or DNA fragments into one type of plasmid. Key advantages of this system include:
- High cloning efficiency
- Reduced false positive rate due to the presence of ccdB gene
- Flexibility in moving the gene of interest into and out of many vectors
- Allowing to maintain desired reading frame and orientation
